I: Renal Embryology:
Embryologic development of the kidney can be described as three distinct entities: pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros.
The pronephros (<4 weeks) and mesonephros (4 – 8 weeks) regress in utero.
The metanephros develops into the kidney.
The ureteric bud originates from the posteromedial aspect of the mesonephric duct where it enters the cloaca.
“Cross talk” between ureteric bud and metanephros = nephrogenesis (complete by 32-34 weeks gestation).
Ureteric bud = ureter, renal pelvis, calyces, collecting ducts
Metanephric blastema = nephrons
Absent vas deferens (mesonephric duct) is associated with ipsilateral renal agenesis.
II: Renal Anatomy:
Flank Incision layers: Latissimus dorsi - external oblique - internal oblique - costal neurovascular bundle - transversus abdominus - transversalis fascia - pararenal fat - Gerota's fascia - perirenal fat - kidney
The costal neurovascular bundle runs along the inferior rib border between the internal oblique muscle and transversus abdominis.
Nearby organs/structures:
Right kidney - Liver, Adrenal Gland, Descending duodenum, hepatic flexure of the colon, psoas muscle, quadratus lumborum
Left kidney - Tail of the pancreas, spleen, adrenal gland, splenic flexure of the colon, psoas muscle, quadratus lumborum
Adrenal glands are located within Gerota's fascia.
Renal artery branches:
Renal artery - segmental - interlobar - arcuate - interlobular - afferent arteriole - glomerulus - efferent arteriole
The first renal artery branch is the posterior segmental artery.
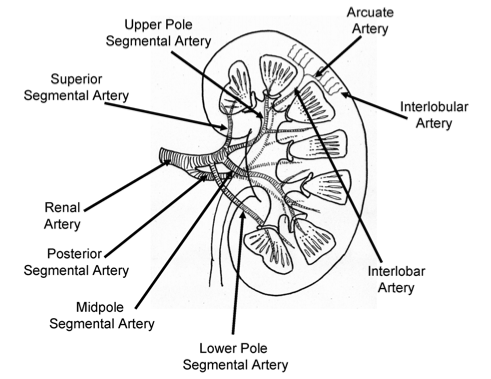
Renal Hilum:
Common sources of bleeding during nephrectomy: right adrenal vein (empties into IVC posteriorly), left lumbar vein (posterior)
Right renal vein short. Left renal vein long, crosses anterior to aorta. Left kidney preferred for renal transplant.
Left gonadal drain to left renal vein. Right gonadal drain to IVC.
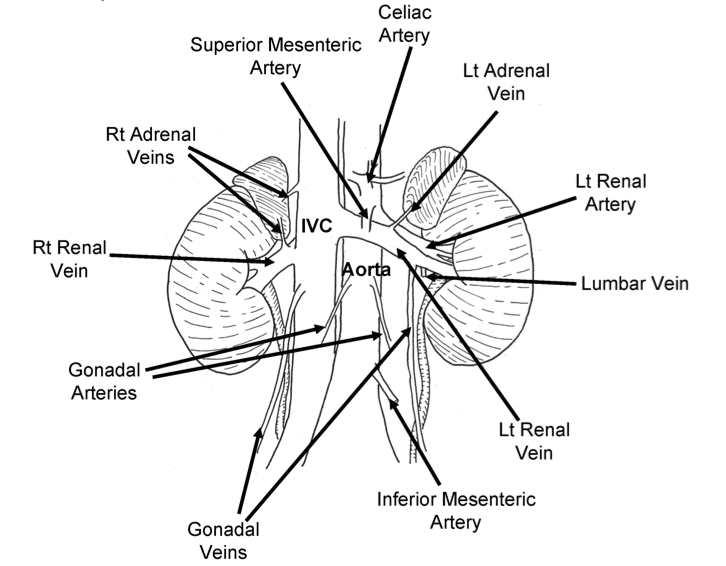
III. Additional Reading:
- Surgical Renal Anatomy. Kim, Isaac Y and Clayman, Ralph V. 40, 2006, AUA Update Series, Vol. 25, pp. 361-368
- Normal and Abnormal Development of the Kidney: A Clinician's Interpretation of Current Knowledge. Glassberg, Kenneth I. 6, 2002, The Journal of Urology, Vol. 167, pp. 2339-2351.