Primary carcinoma of urethra + urothelial carcinoma of prostate
- Epithelium of urethra transitions from stratified squamous to pseudostratified columnar to urothelium (transitions in membranous urethra); cancer will be SCC in urethra distal to membranous, and adenocarcinoma proximal to membranous
| Urethra | Prostate urothelial ca | |
| Ta | non-invasive papillary | |
| Tis | CIS | CIS of prostatic urethra or periurethral or prostatic ducts without stromal invasion |
| T1 | sub-epithelial tissue | |
| T2 | corpus spongiosum or periurethral muscle | prostatic stroma |
| T3 | corpus cavernosum or anterior vagina | periprostatic fat |
| T4 | adjacent organs (e.g. bladder wall, rectal wall) | |
| N1 | single node in inguinal, pelvic, or presacral region | |
| N2 | multiple regional lymph nodes | |
Benign urethral lesions
- In women: urethral caruncle, diverticulum, Skene's gland cyst
- Urethral condyloma - observation OK for small lesions.
- Multimodal treatment - intraurethral 5-FU +/- holmium laser ablation.
- 5-FU in jelly- qweek x 6wk, 6 wk hiatus, then repeat 6-week cycle
- Leiomyoma - most common in reproductive age women; can grow during pregnancy and regress postpartum
- Hemangioma - more common in men; bluish sessile lesion
- Fibroepithelial polyp - more common in men; smooth pink/tan tumors on a stalk
- Inguinal node exam for urethral ca (LN drainage of anterior/distal urethra -> inguinal nodes; proximal/posterior urethra -> external iliac and pelvic nodes)
- Unlike penile cancer, no survival benefit for ILND for urethral cancer if clinically N0, even if T3 disease.
Urethrectomy anatomy
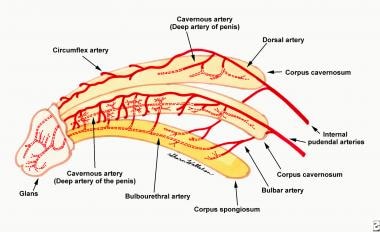
Urethral blood supply
- Blood supply: internal iliac/hypogastric → internal pudendal → common penile → cavernosal, bulbar/urethral, deep dorsal (spongiosum).
- To anterior urethra, primary supplies are bulbar/urethral arteries; deep dorsal also contributes via retrograde flow through glans anastomoses arteries if the spongiosum/artery is transected (but circumflex arteries will be disrupted).

Picture - Wiki - perineal hernia
- Chest XR or CT
- MRI pelvis with/without contrast
Urethral cancer
- < T2 - TUR +/- intraurethral chemotherapy or BCG
- T2 female - chemo/XRT vs cystectomy+urethrectomy vs distal urethrectomy.
- Recurrence - systemic therapy vs chemo/XRT vs pelvic exent
- T2 male
- Fossa/penile urethra - treat with distal urethrectomy vs partial penectomy.
- - margins: survey
- + margins: chemo/XRT (preferred) vs surgery vs XRT
- Recurrence: systemic therapy +/- total penectomy +/- XRT
- Bulbar/membranous urethra - urethrectomy +/- cystoprostatectomy
- pT1/pT2 and N0 - surveil with cystoscopy
- pT3+ or N+ - consider chemo +/- XRT
- Recurrence: systemic therapy +/- XRT
- Fossa/penile urethra - treat with distal urethrectomy vs partial penectomy.
- T3-T4N0 - chemo +/- consolidative surgery; XRT alone
- If UC - also consider NAC + consolidative surgery or radiation
- If non-UC - also consider surgery alone
- Node positive - chemo/XRT +/- consolidative surgery. SCC - prefer chemo/XRT.
- Metastatic disease - include brain in staging imaging; molecular testing for FGFR alterations; systemic tx with gem/cis or DD-MVAC
Urothelial carcinoma of prostate
- Ta/Tis - TURP + BCG
- Recurrence: cystoprostatectomy +/- urethrectomy
- T1 (ductal) - RC +/- urethrectomy vs TURP + BCG
- T2 (stromal) - +/- neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemo; RC +/- urethrectomy
NCCN guidelines 4.2024 - bladder, PCU (page 58)