Symptomatic if < 14 Fr
Etiologies
- Posterior urethra: bladder neck, prostatic, membranous urethra (encircled by striated urinary sphincter)
- Posterior stricture risk factors: pelvic fracture, prostate surgery, pelvic radiation (called stenosis)
- Anterior urethra in corpus spongiosum (penile): bulbar urethra (membranous to peno-scrotal junction; more dorsal)), pendulous/penile urethra (more central/ventral), fossa navicularis (glans), urethral meatus
- Anterior stricture risk factors: iatrogenic, trauma, gonococcal urethritis, lichen sclerosus/balanitis xerotica obliterans, radiation.
Dorsal = anterior
|
|
Female urethra
- Urethra length - 3.5-4 cm
- Sphincter located at mid-urethra, horseshoe-shaped
Anatomy
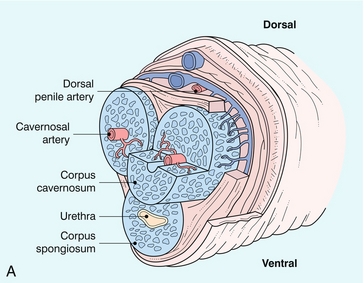
- Blood supply: internal iliac/hypogastric → internal pudendal → common penile → cavernosal, bulbar/urethral, deep dorsal (spongiosum).
- To anterior urethra, primary supplies are bulbar/urethral arteries; deep dorsal also contributes via retrograde flow through glans anastomoses arteries if the spongiosum/artery is transected (but circumflex arteries will be disrupted). But avoid anastomotic urethroplasty if hypospadias (absent vascular connection).
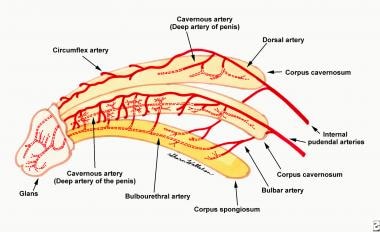
- Blood supply to skin:
- penis/foreskin, anterior scrotum = external pudendal (femoral)
- posterior scrotum = internal pudendal (internal iliac)
Assess stricture with urethrogram
- RUG (retrograde) and VCUG (voiding)
- Membranous urethra is located at bottom of obturator foramen - not a stircture!
Anterior urethral strictures
Urethral dilation
Urethrotomy (DVIU)
- Incise ventral surface at 8-4, or at meatus at 6 oclock.
- Bulbar urethra - more anterior in spongiosum; 12 o'clock incision risks perforation. Penile urethra - corpora are also located at 10-2 o'clock position
- May be used as initial therapy, but high rate of re-stricture (20-30% long-term success rate after 1st DVIU; falls to 0% after 3 or more) - should not perform repeat urethrotomy
- Most favorable if: single stricture < 1-2 cm long, bulbar location (50-70% success rate for 1st DVIU treatment)
- Catheter x 72h (no diff in outcomes between 1-10 days of catheter)
No difference in outcomes between dilation vs DVIU, laser vs cold vs hot knife DVIU (though thermal injury from laser/hot knife can make recurrent stricture more complicated)
Urethral stents - only for bulbar strictures who are not surgical candidates/cannot have other methods
Urethroplasty
- Anastomotic (aka EPA excision and primary anastomosis) - bulbar strictures, posterior pelvic fracture injuries. If used in penile urethra, will cause penile shortening and chordee. Best for 1-2 cm long
- Ideally get to 26Fr with Bougie
- Must preserve bulbar artery; mobilized from perineal body
- Can mobilize to level of suspensory ligament (don't cut the ligament); separate crura of corpora; inferior pubectomy; route urethra around corpora (corporal transposition)
- Harris post-op: 16Fr Foley, 18Fr SPT until VCUG in 4 weeks. Macrobid 100 mg BID while catheters. Penrose out POD1. D/c POD1.
- Enemchukwu: catheter 2 weeks if EPA, 3 weeks if augment
- Augmentation (onlay - non-circumferential (success rate similar regardless of location) vs. tubularized/substitution) - onlays have higher success rate. Can be used anywhere
- Flaps (eg penile skin with epithelium facing into urethral lumen).
- Graft - no blood supply, imbibition from graft bed until inosculation. Buccal mucosa generally preferred.
- Complications: re-stricture, penile shortening/chordee/deviation, ED (< 5%, generally resolves within 6 mo), ejaculatory dysfunction (20%) (bulbospongiosus dysfunction/propulsion after EPA with sponge transection), post-void dribbling for same reason, diverticulum (reduced risk with graft instead of flap; dorsal onlay so that the cavernosa keeps things in place). Success rate 86% at 5 yrs but does not deteriorate for anastomotic reconstruction. Augmentation falls to 58% at 15 yrs.
Bladder neck contracture
- TUIBN (transurethral incision of bladder neck); full-thickness incision at 5 and 7-o'clock. Foley x 3-5/7d afterwards.
- Side effect - retrograde ejaculation. Can do unilateral incision with 50% success rate, 10% retrograde ejaculation
- Female urethroplasty options (e.g. Blandy flap)