|
Dosing |
Notes |
||
|
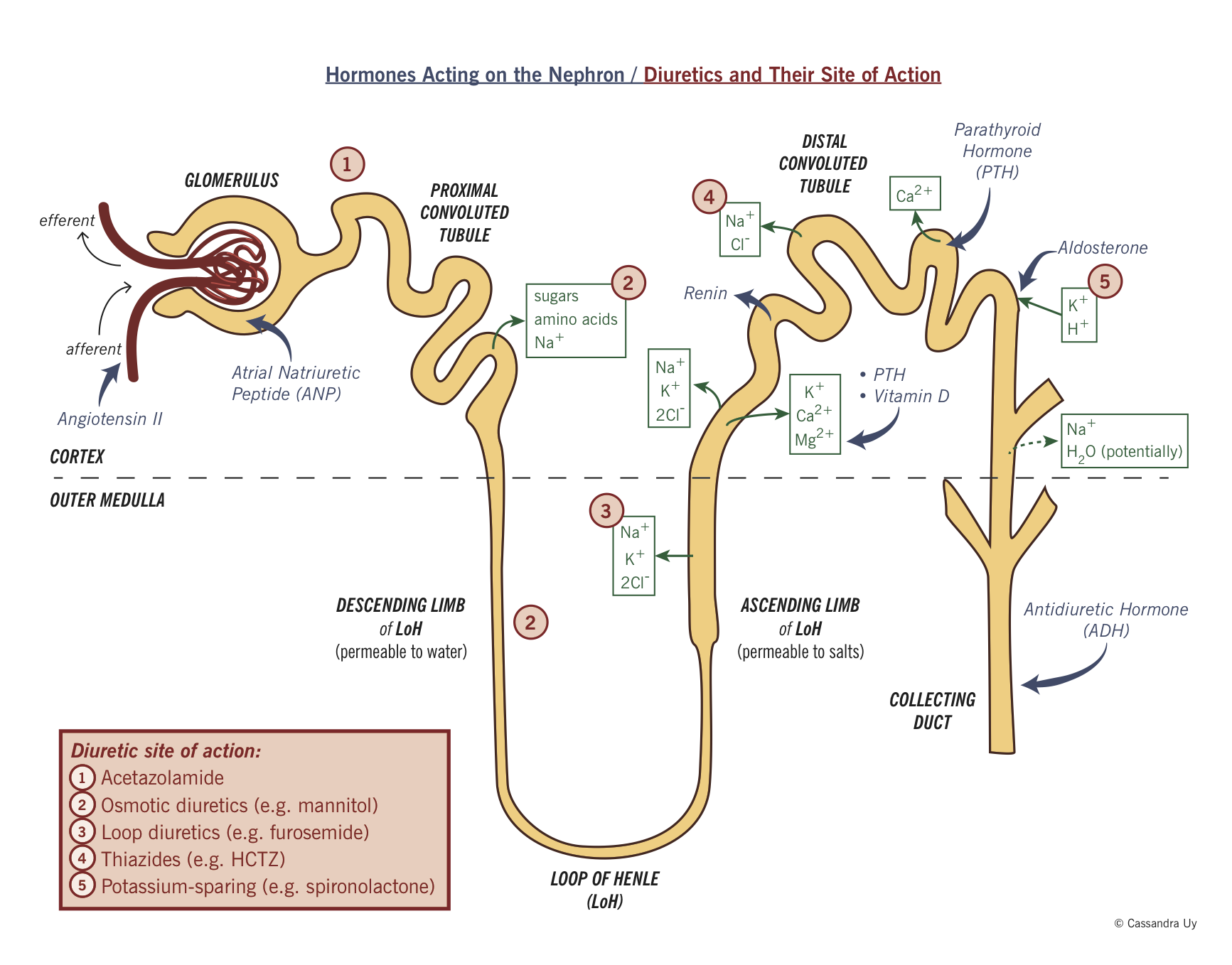
Loop diuretics (Na, K, 2 Cl) (thick ascending limb of Loop of Henle) |
|||
|
Furosemide |
Starting dose 20-40 mg (IV) |
PO bioavailability low (50%) and extremely variable - 10-100% 6 hour duration |
Excrete 20-25% of total filtered Na (first-line) Reduced PO absorption with intestinal mucosal edema → IV route preferred if very fluid overloaded |
|
Torsemide |
Starting dose 5-10 mg |
Long half-life Good PO bioavailability |
|
|
Bumetanide |
Starting dose 0.5-1 mg |
Good PO bioavailability |
|
|
Aldosterone antagonist (K+ sparing) (cortical collecting tubule) |
|||
|
Spironolactone (eplenerone fewer side effects, more $) |
Starting dose 12.5 – 25 mg QD (Aldactone:Lasix = 100:40 for electrolyte balance) |
Recommended in (improves remodeling):
|
Excrete 1-2% of total filtered Na 30% reduction in mortality for HFrEF |
|
Thiazide diuretics (Na, Cl) (distal convoluted tubule) |
|||
|
Metolazone (PO only) (used on top of loop diuretic) |
Low dose (< 5 mg) effective Up to 250 mg |
PO thiazide should precede IV loop diuretic by 2-5 hours Also acts in proximal tubule - better than other thiazides at diuresing with low GFR |
Excrete 3-5% of total filtered Na Distal tubule can reabsorb 75-80% of Na from the loop of Henle |
- 40 mg IV furosemide = 80 mg PO furosemide = 1 mg IV/PO bumetanide = 20 mg IV torsemide
- Diuretic effect reaches steady state after ~ 2 weeks (so electrolyte abnormalities will also stabilize in first 2-4 weeks)
- Maximum natriuretic response occurs with first dose
- Bolus and continuous infusion are similar
- Thiazides can cause hyponatremia compared to loop diuretics - loop diuretics disrupt the hyperosmotic medullary gradient and therefore impair ADH response, while sodium excretion by thiazide diuretics can be compensated for by ADH-mediated free water reabsorption -> hyponatremia
- Thus, use thiazides (e.g. metolazone) when diuresing in hypernatremia