FAST (focused assessment with sonography in trauma)
Indications
- Blunt/penetrating trauma to abdomen/chest
- Trauma in pregnancy (no radiation)
- Unexplained hypotension
Uses
- Rapid, portable test to triage trauma patients
- Looking for fluid in the abdomen/heart/lungs
- Hemoperitoneum: sens. 76-90%, spec. 95-100%
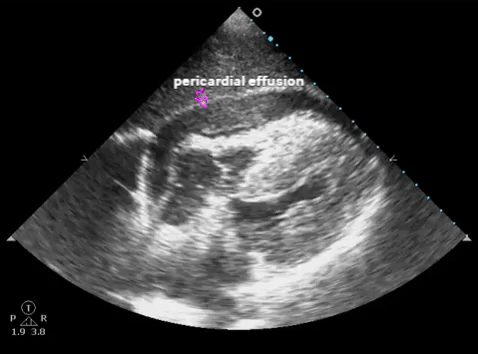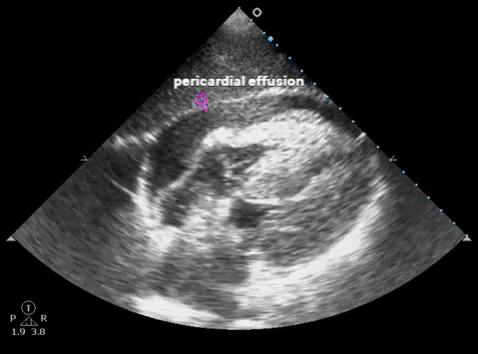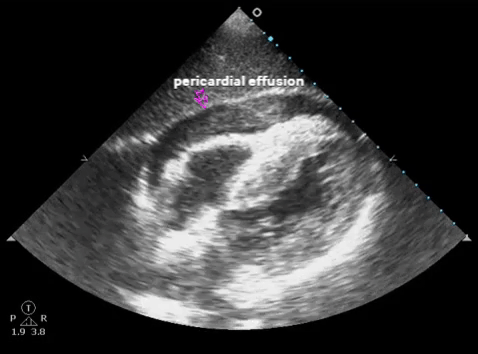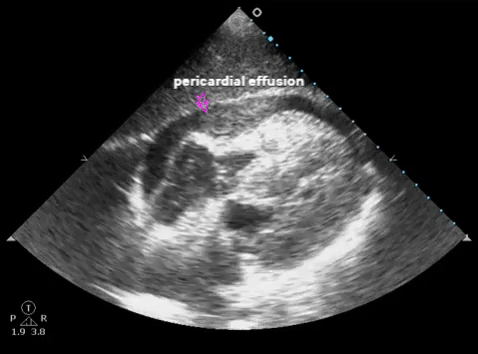
- Pericardial effusion/hemothorax: sens. ~100%
- Pneumothorax: sens. 88%, spec. 99% (vs. CXR sens. 52%)
Limitations
- Typically does not identify source of bleeding
- Not great at detecting bowel/mesentery injuries
- Difficult to assess retroperitoneum
- Limited by body habitus
- Use curvilinear probe
| View | Normal | Abnormal |
|
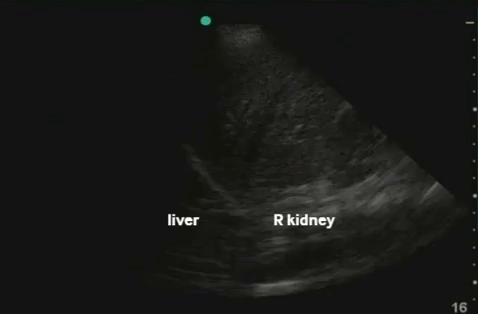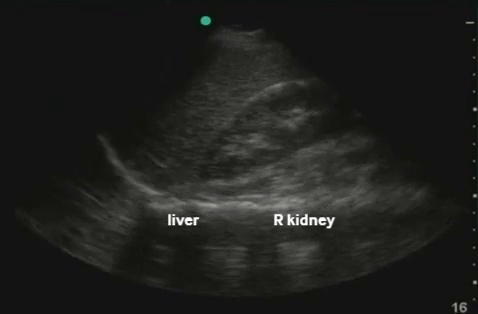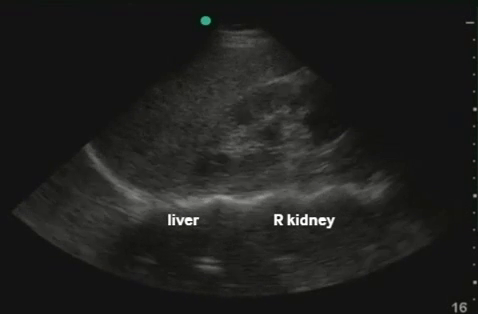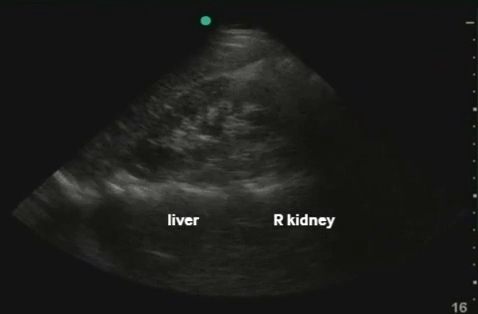
RUQ: liver, kidney - Morisson's pouch Need to get liver edge for full view. Extend upwards to look for hemothorax |
 |
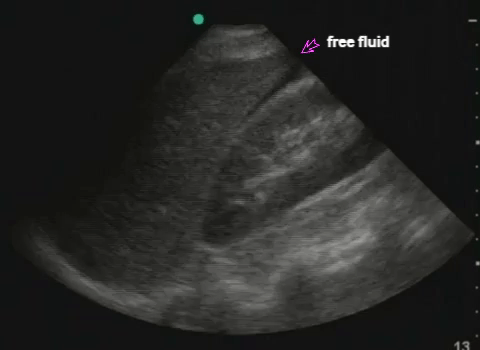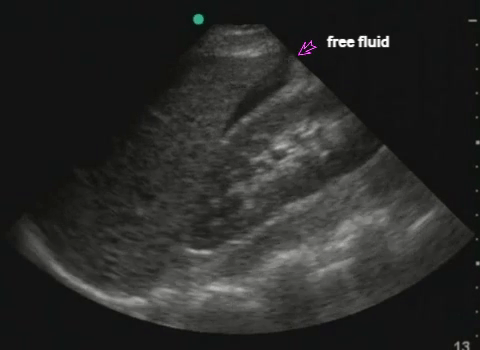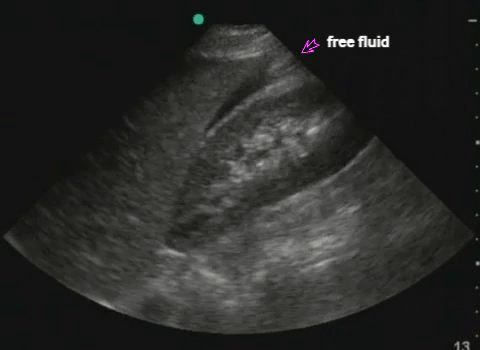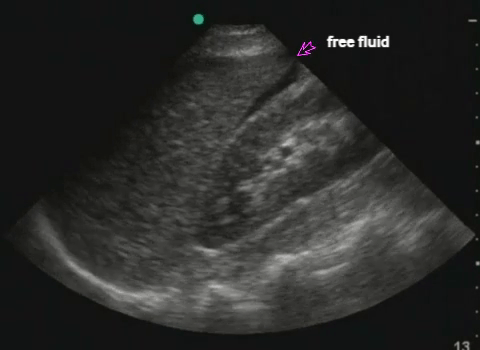 |
|
LUQ: spleen, kidney Extend upwards to look for hemothorax |
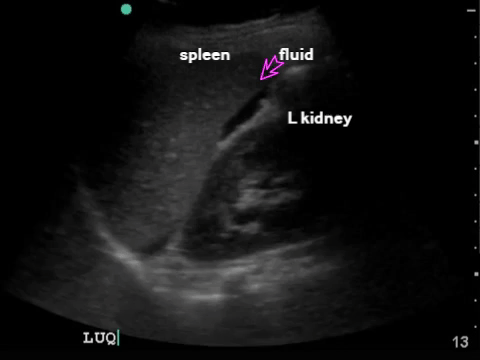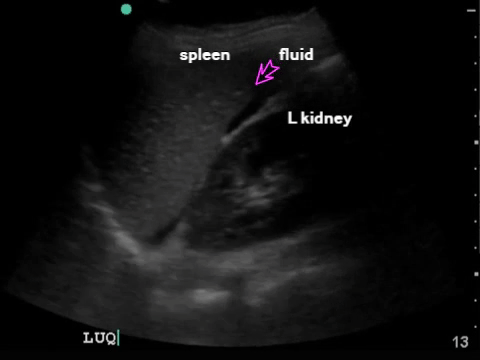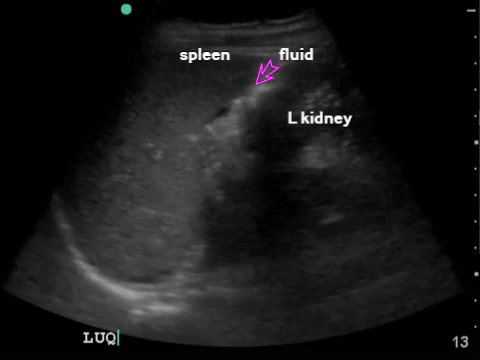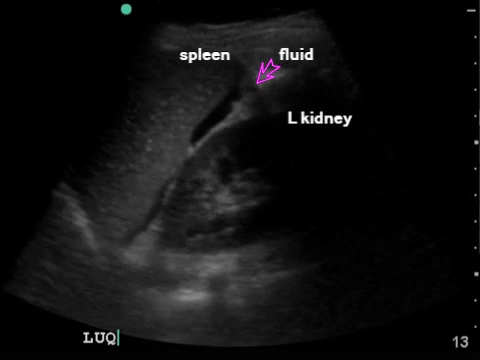 |
|
| Pelvis: transverse | 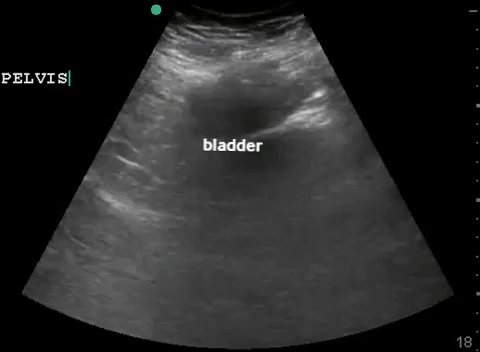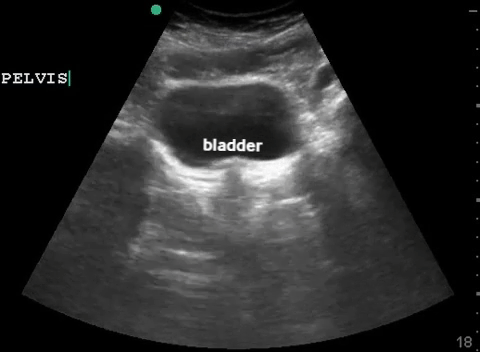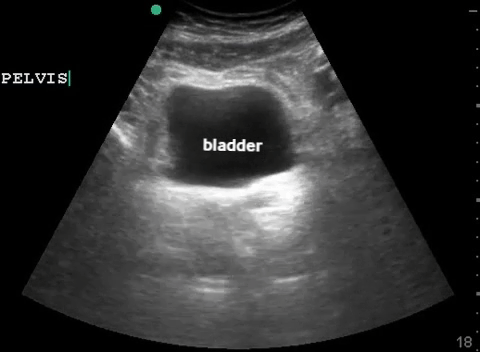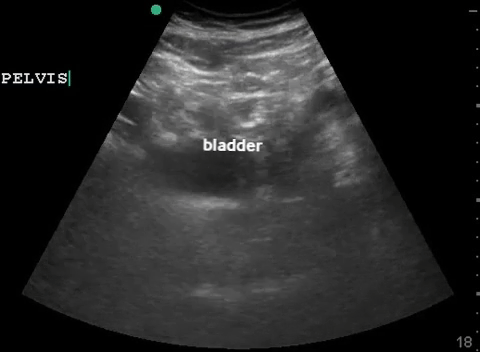 |
|
| Pelvis: sagittal | 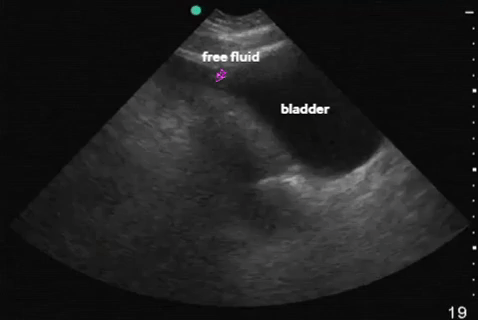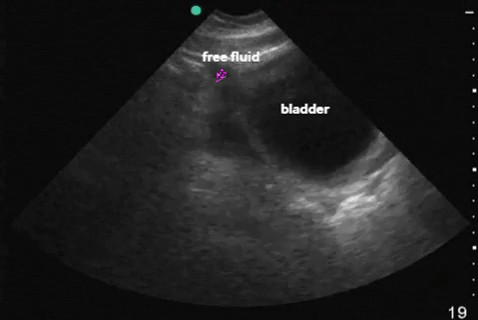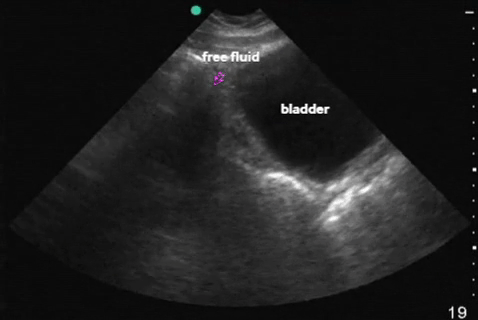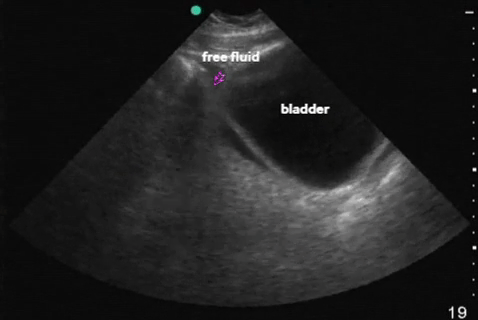 |
|
| Subxiphoid - heart, pericardium | 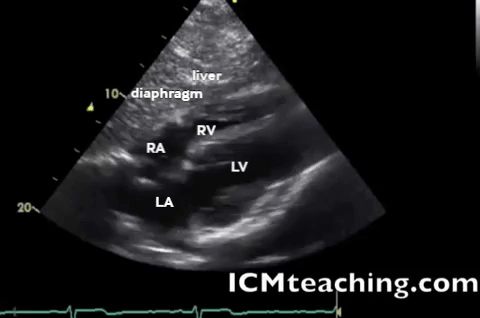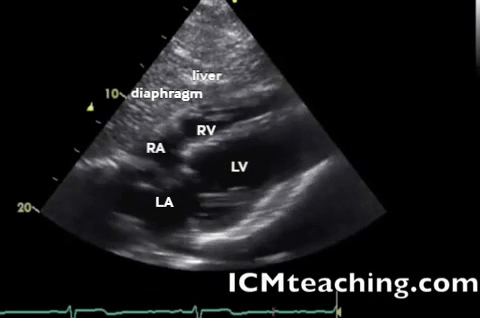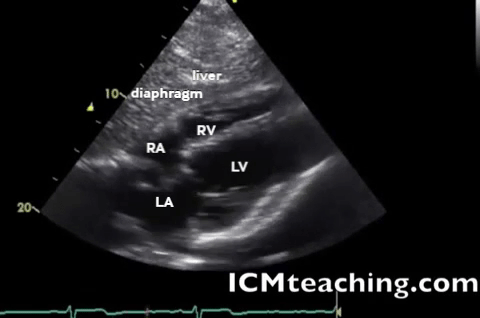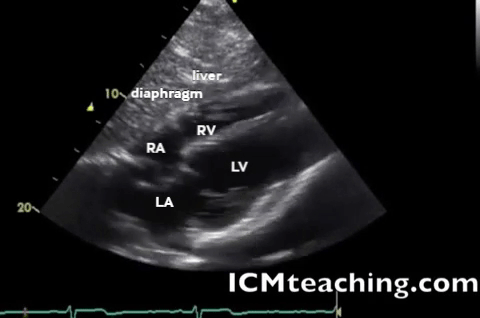 |
 |
| extended FAST (eFAST) | ||
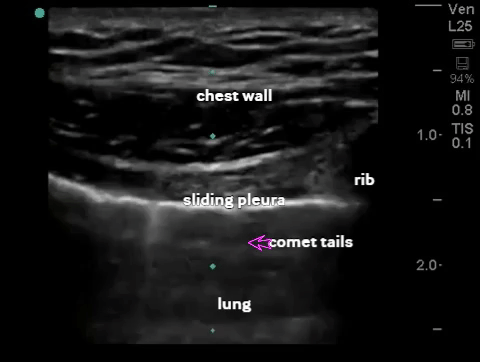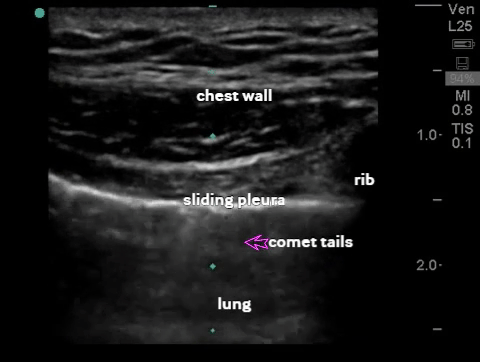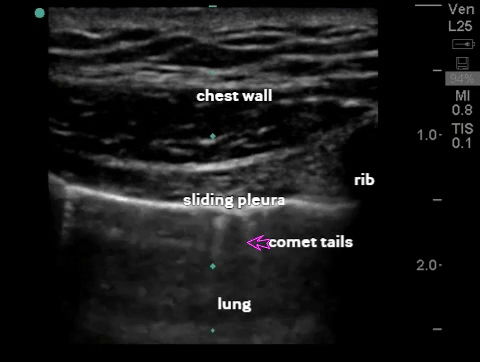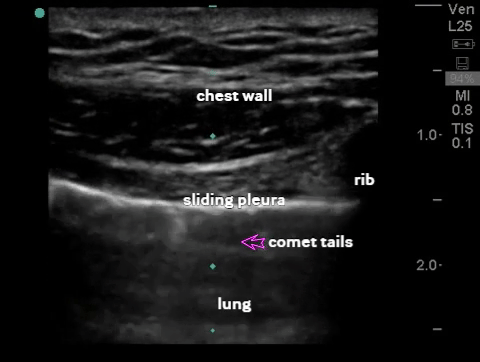
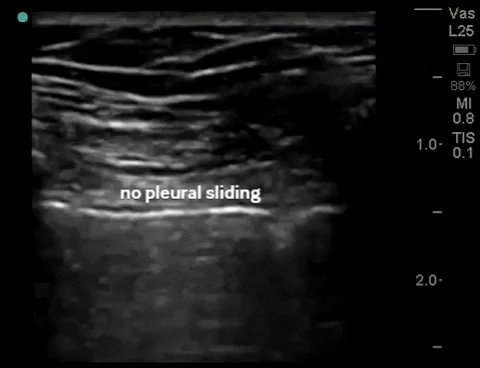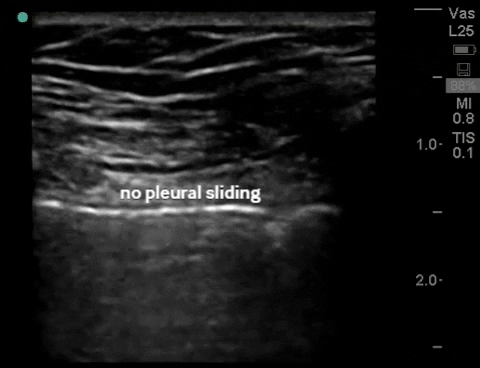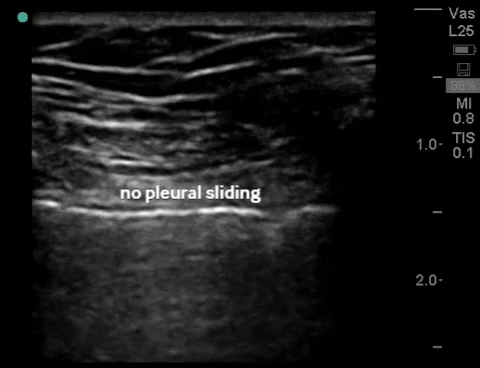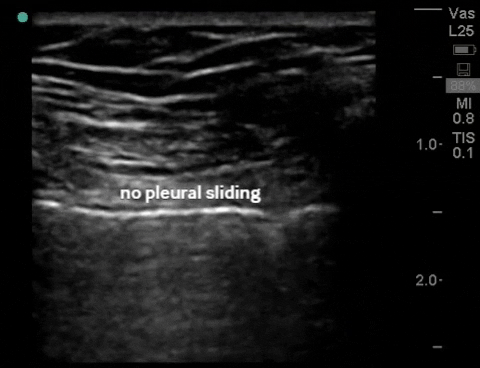
| Thorax - pneumothorax (2-3 views per lung) |
B-mode: comet tail, sliding sign (visceral/parietal pleura slide against each other) |
B-mode: no sliding (air from pneumothorax disrupts pleural interface) |
|
M-mode: "sandy beach" (motion of sliding pleura is detected) |
M-mode: "barcode"/"stratosphere", (no motion detected) |
|
| Stable | Unstable | |
| (+) FAST | CT | OR |
| (-) FAST | CT | Panic |